Unveiling the Backlit Sensors in Camera Technology
Posted by Mike Thomas on 3rd Aug 2023
One significant breakthrough that revolutionized low-light photography is the development of backlit sensors. In this blog, we will delve into the history, manufacture, and the remarkable benefits of backlit sensors in modern cameras.
A Glimpse into History:
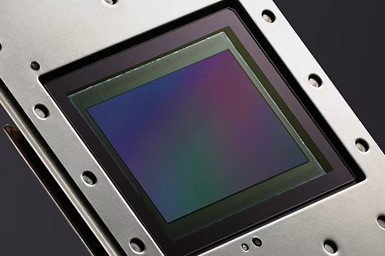
Backlit sensors, also known as back-illuminated or backside-illuminated (BSI) sensors, made their debut in the early 2000s. Their invention was a remarkable step forward in addressing the limitations of traditional front-illuminated sensors. Backlit sensors were initially employed in scientific and industrial applications before eventually finding their way into professional and consumer cameras. Traditional front-illuminated sensors have a layer of circuitry positioned in front of the photodiode layer, leading to a reduction in light-gathering efficiency. In contrast, backlit sensors feature a clever rearrangement of the sensor's architecture. The photodiodes are positioned at the back of the sensor, allowing light to pass through a transparent layer of wiring and other circuitry, directly reaching the photodiodes. This fundamental change results in significantly increased light sensitivity.
The manufacture of backlit sensors involves intricate processes and cutting-edge technology. Specialized semiconductor fabrication techniques are employed to create the sensor's layers with precision. The process involves depositing various materials onto a silicon wafer, including metal and silicon oxide layers, to create the necessary circuitry and light-sensitive elements. Additional steps such as micro-lens formation and colour filter deposition follow, ensuring the sensor captures accurate colour information.
Advantages:
a. Enhanced Low-Light Performance: The primary advantage of backlit sensors is their exceptional low-light performance. By eliminating the obstructions caused by circuitry, these sensors allow more light to reach the photodiodes, resulting in improved sensitivity and reduced noise in low-light environments. This capability enables photographers to capture beautifully detailed images even in challenging lighting conditions.
b. Increased Dynamic Range: Backlit sensors exhibit an expanded dynamic range, enabling them to capture a wider range of tones from shadows to highlights. This increased latitude empowers photographers to retain more detail in both dark and bright areas, delivering more balanced and visually appealing images.
c. Improved Image Quality: With their enhanced light-gathering capabilities and reduced noise levels, backlit sensors contribute to overall image quality. The improved signal-to-noise ratio ensures cleaner and crisper images, particularly in higher ISO settings.
d. Faster Autofocus and larger frame Rates: The efficiency of backlit sensors allows for faster autofocus speeds and higher frame rates. The increased sensitivity enables cameras to acquire focus quickly, resulting in sharper images. Additionally, the improved data readout speed of backlit sensors enables faster continuous shooting, making them well-suited for capturing action and sports footage.
Manufacture of Back Lit sensors was expensive due to a high fail rate. This prohibited them being used in all but the most expensive cameras. Now it would seem manufacturers have sorted these limitations and we see them in cameras such as the new Sony Alpha 6700.
Conclusion:
Backlit sensors have significantly elevated the capabilities of modern cameras, enabling photographers to capture exceptional images even in challenging lighting conditions. With their enhanced low-light performance, increased dynamic range, and improved image quality, these sensors have become a valuable asset for both professionals and enthusiasts. As technology continues to evolve, it's exciting to anticipate how backlit sensors will evolve further and shape the future of cameras, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in capturing the world around us.